The Complete Lean Startup Method Guide: 7 Proven Steps Every Beginner Must Know
Starting a business can feel like navigating through a minefield blindfolded. The harsh reality is that approximately 90% of startups fail, with most entrepreneurs discovering too late that they’ve built something nobody actually wants. This devastating statistic led to the revolutionary lean startup method – a systematic approach that has transformed how successful companies are built.
The lean startup method isn’t just another business buzzword; it’s a proven framework that has helped countless entrepreneurs avoid costly mistakes while building products customers actually love. As entrepreneur Steve Blank famously said, “No business plan survives first contact with customers.” Whether you’re a first-time founder or an experienced professional looking to launch your next venture, understanding this methodology can mean the difference between joining the 90% who fail and the 10% who succeed.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the lean startup method through seven essential steps, real-world examples, and practical applications that you can implement immediately. By the end, you’ll have a clear roadmap for applying lean principles to your own entrepreneurial journey.
What is the Lean Startup Method?
The lean startup method is a scientific approach to creating and managing startups, developed by entrepreneur Eric Ries in his groundbreaking 2011 book “The Lean Startup.” This methodology draws inspiration from lean manufacturing principles pioneered by Toyota, adapting them specifically for the uncertain, fast-paced world of startups.
At its core, the lean startup method operates on a fundamental principle: entrepreneurs should validate their business ideas with real customers before investing significant time and resources. This approach dramatically reduces the risk of building products that nobody wants while accelerating the path to finding a viable business model.
The method revolves around three key activities: Build, Measure, and Learn. This continuous cycle helps entrepreneurs navigate uncertainty by quickly testing ideas, measuring results, and making data-driven decisions about what to build next.
“The only way to win is to learn faster than anyone else.” – Eric Ries
Understanding the Core Philosophy Behind the Lean Startup Method
Traditional business planning often involves creating detailed business plans, conducting extensive market research, and developing fully-featured products before launch. The lean startup method challenges this approach by acknowledging that startups operate under conditions of extreme uncertainty where traditional planning methods often fail.
Instead of trying to predict the future, the lean startup method teaches entrepreneurs to conduct experiments that test specific hypotheses about their business model. This scientific approach transforms entrepreneurship from a leap of faith into a systematic process of discovery and validation.
The methodology recognizes that customer behavior is often unpredictable, market conditions change rapidly, and initial assumptions are frequently wrong. By embracing these realities, the lean startup method provides tools for adapting quickly and efficiently to market feedback.
The 5 Fundamental Principles of the Lean Startup Method
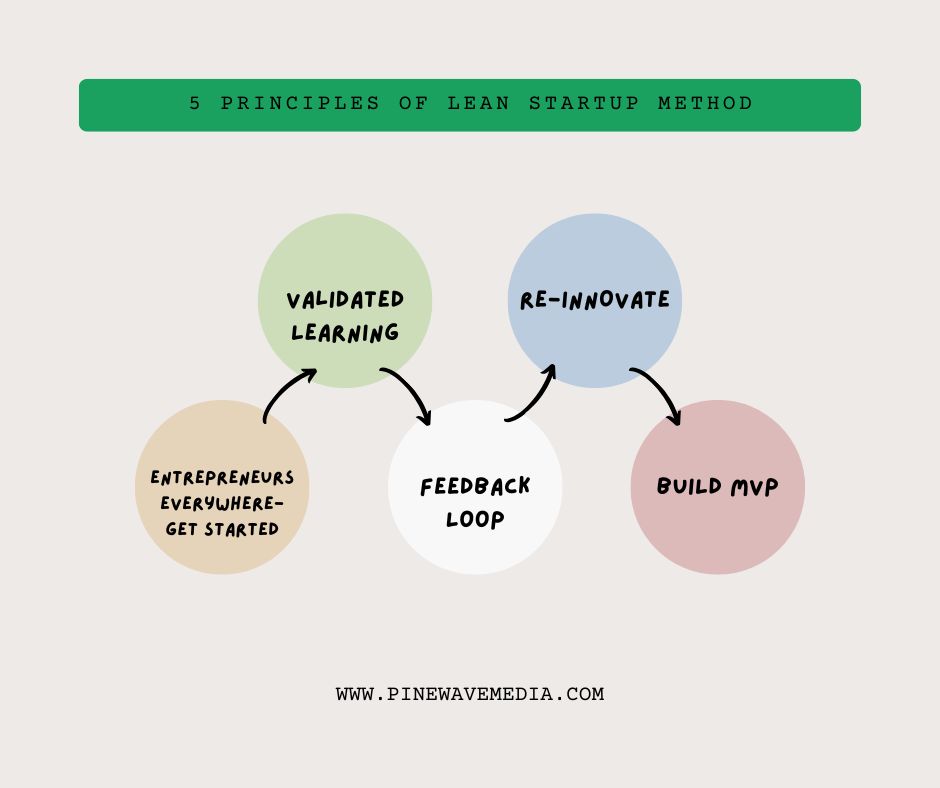
1. Entrepreneurs Are Everywhere
The lean startup method recognizes that entrepreneurship isn’t limited to Silicon Valley garages or venture-backed companies. Anyone working under conditions of extreme uncertainty to create something new qualifies as an entrepreneur, whether they’re inside a Fortune 500 company or starting from their kitchen table.
This principle democratizes innovation and acknowledges that the lean startup method applies across industries, company sizes, and geographical locations. Corporate intrapreneurs, social entrepreneurs, and traditional small business owners can all benefit from lean principles.
2. Validated Learning
Traditional education teaches us to avoid failure, but the lean startup method reframes failure as a learning opportunity. Validated learning means using scientific experiments to test business hypotheses and learn from the results, whether positive or negative.
This principle transforms the startup process from a faith-based initiative into a data-driven endeavor. Instead of making assumptions about what customers want, entrepreneurs following the lean startup method design specific experiments to test their beliefs against reality.
3. Build-Measure-Learn Feedback Loop
The heart of the lean startup method lies in this continuous cycle. Entrepreneurs build minimal experiments, measure how customers respond, and learn from the results to inform their next steps. This feedback loop accelerates learning while minimizing wasted effort and resources.
The key insight is that the goal isn’t to build the perfect product immediately, but to learn as quickly and efficiently as possible. Each iteration through the Build-Measure-Learn cycle brings entrepreneurs closer to a sustainable business model.
4. Innovation Accounting
Traditional accounting methods don’t work well for early-stage startups because revenue and profit margins are often non-existent. The lean startup method introduces innovation accounting – a framework for measuring progress when conventional metrics don’t apply.
Innovation accounting focuses on learning milestones rather than financial milestones. Metrics might include customer acquisition rates, engagement levels, or conversion percentages that indicate whether the startup is moving toward a viable business model.
5. Minimum Viable Product (MVP)
Perhaps the most well-known concept from the lean startup method, the MVP represents the simplest version of a product that can test core business hypotheses. It’s not about building a cheap or low-quality product, but rather identifying the minimum features needed to start the learning process.
The MVP concept challenges entrepreneurs to resist the urge to build comprehensive solutions before understanding customer needs. By starting small and iterating based on feedback, startups can avoid over-engineering while discovering what customers actually value.
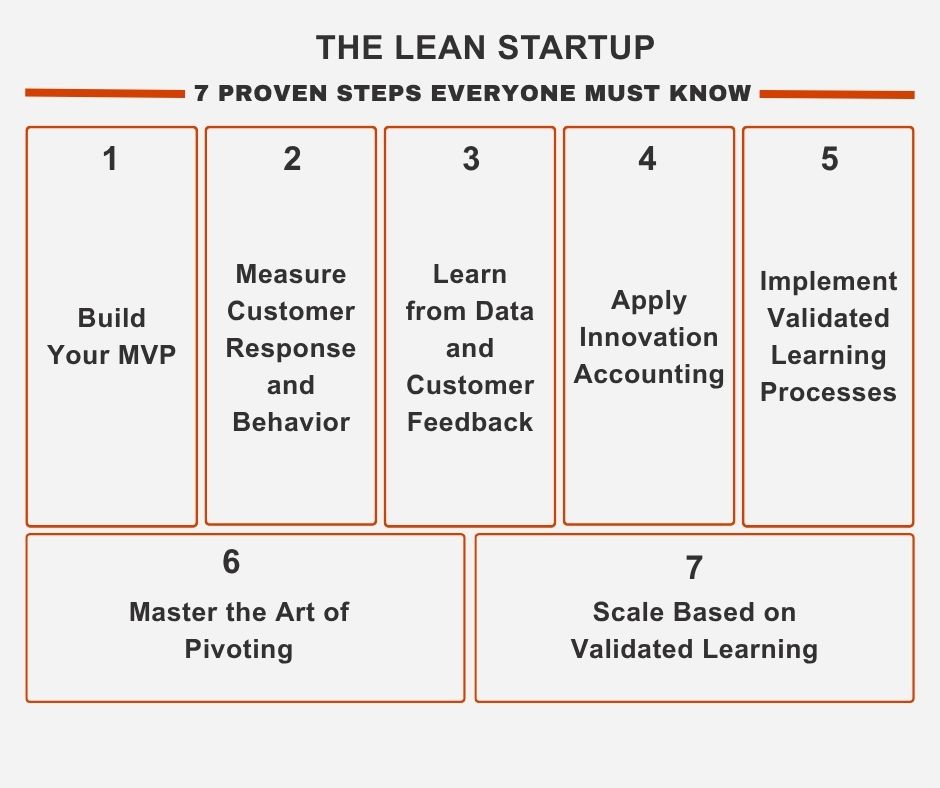
Step 1: Build Your Minimum Viable Product (MVP)
The first step in applying the lean startup method involves creating an MVP that tests your core business hypothesis. Your MVP should focus on solving one specific problem for a clearly defined customer segment, using the minimum features necessary to deliver value.
Consider Dropbox’s famous MVP story. Instead of building complex file-syncing software, founder Drew Houston created a simple three-minute video demonstrating how the product would work. This video validated customer demand before writing a single line of production code, saving months of development time.
Your MVP might take various forms depending on your business model. It could be a landing page describing your service, a manual process that simulates automation, or a basic version with just one key feature. The lean startup method emphasizes that perfection is the enemy of progress – launch something small and learn from real customer interactions.
Step 2: Measure Customer Response and Behavior
Once your MVP is in customers’ hands, the lean startup method requires systematic measurement of their responses and behaviors. Focus on actionable metrics that reveal whether customers find genuine value in your offering, rather than vanity metrics that simply make you feel good.
Key metrics to track include user engagement rates, conversion percentages, customer retention statistics, and qualitative feedback about user experience. These measurements provide concrete data about whether your value proposition resonates with your target market.
The lean startup method warns against common measurement mistakes, such as focusing on downloads or page views without understanding user behavior. Instead, track metrics that correlate with long-term customer value and business sustainability.
Step 3: Learn from Data and Customer Feedback
The learning phase represents where the lean startup method transforms data into actionable insights. Analyze your measurements to understand what’s working, what isn’t, and why customers behave the way they do.
This analysis leads to one of two critical decisions: pivot or persevere. Pivoting means making a fundamental change to your business model, target customer, or core product based on what you’ve learned. Persevering means continuing on your current path while making incremental improvements.
The lean startup method emphasizes that both decisions should be driven by data, not emotions or sunk costs. Many successful companies, including Twitter and Instagram, achieved success only after pivoting from their original concepts based on customer learning.
Step 4: Apply Innovation Accounting
Traditional financial metrics often don’t provide meaningful insights for early-stage startups. The lean startup method introduces innovation accounting to track progress toward a sustainable business model using learning-focused metrics.
Innovation accounting typically involves three levels of metrics: actionable metrics that demonstrate clear cause-and-effect relationships, accessible metrics that everyone on the team can understand, and auditable metrics that can be reproduced and verified.
Examples might include the cost of acquiring customers, the percentage of customers who become active users, or the rate at which users refer new customers. These metrics help startups following the lean startup method make informed decisions about resource allocation and strategic direction.
Step 5: Implement Validated Learning Processes
Validated learning distinguishes the lean startup method from traditional trial-and-error approaches. Instead of making random changes and hoping for improvement, validated learning involves forming specific hypotheses and designing experiments to test them systematically.
Each experiment should test a specific assumption about your business model, customer behavior, or value proposition. Document your hypotheses before running experiments, define success criteria in advance, and analyze results objectively regardless of whether they support your initial beliefs.
The lean startup method teaches that negative results are just as valuable as positive ones because they prevent you from pursuing ineffective strategies. Failed experiments guide you away from dead ends while successful ones point toward promising directions.
Step 6: Master the Art of Pivoting
Pivoting represents one of the most challenging aspects of the lean startup method because it requires entrepreneurs to abandon ideas they’ve invested time and energy developing. However, successful pivots often separate thriving companies from failed ones.
The lean startup method identifies several types of pivots, including customer segment pivots (targeting a different market), problem pivots (solving a different problem), and solution pivots (changing how you solve the problem). Each type addresses different aspects of your business model based on learning and feedback.
Timing your pivot correctly requires careful attention to your metrics and honest assessment of your progress. The lean startup method suggests pivoting when you’re not making sufficient progress toward your goals despite genuine effort and multiple iterations.
Step 7: Scale Based on Validated Learning
Once you’ve validated your business model through the lean startup method, you can begin scaling with confidence. Scaling too early represents one of the most common startup mistakes, but the lean approach helps you avoid this trap by ensuring product-market fit before growth.
Validated learning provides the foundation for sustainable scaling because you understand your customers, your value proposition, and your business model mechanics. This knowledge enables more efficient marketing, better product development decisions, and smarter resource allocation.
The lean startup method continues to apply during the scaling phase, but the experiments become larger and more sophisticated. Instead of testing basic assumptions, you might experiment with pricing strategies, distribution channels, or feature prioritization based on customer segments.
Real-World Success Stories of the Lean Startup Method
Airbnb’s Lean Beginning
Airbnb’s founders exemplify the lean startup method in action. They started by renting out air mattresses in their apartment during a design conference, testing whether people would actually pay to stay in strangers’ homes. This simple experiment validated their core assumption before building any technology platform.
The founders continued applying lean startup method principles by creating a simple website, gathering feedback from early users, and iterating based on what they learned. They didn’t build a comprehensive platform immediately; instead, they validated demand through increasingly sophisticated experiments.
Twitter’s Pivot Success
Twitter began as a side project within Odeo, a struggling podcasting company. When Apple announced iTunes would support podcasts, the Odeo team realized their original business model was doomed. Following lean startup method principles, they analyzed user behavior and noticed heavy engagement with their internal communication tool.
The team pivoted to focus entirely on this short messaging feature, eventually becoming Twitter. This pivot demonstrates how the lean startup method can reveal unexpected opportunities even when original plans fail.
Buffer’s Transparent Journey
Buffer, the social media scheduling tool, has openly documented their application of the lean startup method from inception through scaling. Founder Joel Gascoigne started with a simple landing page describing the product concept, measuring customer interest before building any software.
Based on positive response, he created a minimal MVP that allowed users to schedule tweets. Buffer continued applying lean startup method principles throughout their growth, experimenting with pricing, features, and market positioning based on customer feedback and data analysis.
Common Mistakes When Applying the Lean Startup Method
The Perfectionism Trap
Many entrepreneurs struggle with launching imperfect products, despite understanding lean startup method principles intellectually. They spend months polishing features and fixing minor bugs while missing opportunities to learn from real customer interactions.
The lean startup method requires accepting that your first version will be imperfect and potentially embarrassing. However, customer feedback on an imperfect product provides more value than internal speculation about a perfect one.
Misinterpreting Customer Feedback
Another common mistake involves cherry-picking feedback that supports preconceived notions while dismissing data that challenges assumptions. The lean startup method requires objective analysis of all feedback, even when it suggests uncomfortable truths about your product or market.
Learn to distinguish between what customers say and what they do. Customer behavior often provides more reliable insights than customer opinions, especially when making product development decisions using the lean startup method.
Failing to Pivot When Necessary
Emotional attachment to original ideas prevents many entrepreneurs from pivoting when evidence suggests change is necessary. The lean startup method teaches that pivoting isn’t failure – it’s intelligent adaptation based on learning.
Set clear criteria for pivot decisions before you become emotionally invested in specific outcomes. This approach helps maintain objectivity when analyzing whether your current direction is working effectively.
Tools and Resources for Implementing the Lean Startup Method
No-Code MVP Development
Modern no-code tools make it easier than ever to create MVPs without technical skills. Platforms like Webflow, Bubble, or Carrd enable rapid prototyping and testing of product concepts following lean startup method principles.
These tools allow entrepreneurs to focus on customer validation rather than technical development during early stages. You can create functional prototypes, collect user feedback, and iterate based on learning before investing in custom development.
Analytics and Measurement Platforms
Google Analytics, Mixpanel, and Amplitude provide insights into user behavior essential for lean startup method implementation. These platforms help track actionable metrics rather than vanity metrics, enabling data-driven decision making.
Survey tools like Typeform, SurveyMonkey, or Google Forms facilitate direct customer feedback collection. Combining quantitative analytics with qualitative surveys provides comprehensive insights for validated learning.
Learning Resources and Communities
Eric Ries’s “The Lean Startup” remains the definitive guide to this methodology. Steve Blank’s “The Four Steps to the Epiphany” provides additional frameworks complementing lean startup method principles.
Online communities like Lean Startup Circle, Founder Groups, and industry-specific forums offer peer support and practical advice for applying lean startup method concepts. These communities provide accountability and learning opportunities from other entrepreneurs’ experiences.
Advanced Lean Startup Method Techniques
Cohort Analysis for Customer Understanding
Advanced lean startup method practitioners use cohort analysis to understand customer behavior patterns over time. This technique involves grouping customers by shared characteristics or experiences, then tracking their behavior longitudinally.
Cohort analysis reveals insights about customer lifetime value, retention rates, and feature adoption that inform product development and business model decisions within the lean startup method framework.
A/B Testing for Optimization
Systematic A/B testing represents a sophisticated application of lean startup method experimentation principles. Instead of making assumptions about user preferences, entrepreneurs can test different versions of features, messaging, or user experiences directly.
Effective A/B testing requires proper statistical design, sufficient sample sizes, and clear success metrics. This approach enables continuous optimization based on validated learning rather than opinion or intuition.
Customer Development Interviews
Customer development interviews provide qualitative insights that complement quantitative metrics in the lean startup method. These structured conversations help entrepreneurs understand customer motivations, pain points, and decision-making processes.
Effective customer interviews require careful preparation, open-ended questions, and active listening. The goal is learning rather than selling, which means entrepreneurs must resist the urge to pitch their product during these conversations.
Adapting the Lean Startup Method for Different Industries
B2B Applications
Business-to-business companies can apply lean startup method principles despite longer sales cycles and more complex decision-making processes. B2B MVPs might involve manual services, pilot programs, or proof-of-concept implementations rather than consumer-facing products.
The key is identifying ways to test core business hypotheses with shorter feedback loops than traditional B2B sales processes. This might involve targeting smaller customers initially or offering limited pilot programs to gather learning quickly.
Physical Product Development
The lean startup method applies to physical products, though the implementation differs from software products. Physical product MVPs might involve 3D printed prototypes, manual assembly processes, or pre-order campaigns that test market demand.
Companies like Pebble smartwatch and Oculus VR successfully used crowdfunding platforms as MVPs, validating customer demand before manufacturing products at scale.
Service-Based Businesses
Service businesses can apply lean startup method principles by testing service concepts with limited markets, manual processes, or pilot programs. The goal remains the same: validate customer demand and optimize service delivery based on feedback.
Professional services firms might test new service offerings with existing clients, while local service businesses might launch in limited geographic areas before expanding.
Measuring Success with the Lean Startup Method
Setting Appropriate Metrics
Success metrics for the lean startup method differ from traditional business metrics because they focus on learning and validation rather than immediate profitability. Early-stage metrics might include customer discovery interviews completed, prototype iterations tested, or user feedback surveys collected.
As startups progress through the lean startup method, metrics evolve to include customer acquisition costs, user engagement rates, and revenue per customer. The key is choosing metrics that provide actionable insights for decision making.
Long-term Impact Assessment
The ultimate measure of lean startup method success is building a sustainable business that creates value for customers. This often takes longer to achieve than traditional metrics suggest, requiring patience and persistence in applying lean principles.
Successful lean startup method implementation results in products that customers love, business models that generate sustainable revenue, and organizations that can adapt quickly to changing market conditions.
The Future of the Lean Startup Method
Evolution and Adaptations
The lean startup method continues evolving as entrepreneurs apply its principles in new contexts and industries. Recent adaptations include lean principles for artificial intelligence development, sustainability-focused businesses, and global scaling strategies.
Emerging technologies like artificial intelligence and machine learning provide new tools for implementing lean startup method experimentation and measurement. These technologies enable more sophisticated customer behavior analysis and faster iteration cycles.
Integration with Modern Business Practices
Modern companies increasingly integrate lean startup method principles with other methodologies like agile development, design thinking, and growth hacking. This integration creates comprehensive approaches to innovation and business development.
The lean startup method has influenced corporate innovation programs, with large companies creating internal incubators and innovation labs that apply lean principles to new product development.
Getting Started with the Lean Startup Method Today

Your First Steps
Begin implementing the lean startup method by identifying your core business hypothesis – the fundamental assumption your business depends on. Then design the simplest possible experiment to test this assumption with real customers.
Document your hypothesis clearly, define success criteria in advance, and commit to analyzing results objectively. This scientific approach distinguishes the lean startup method from random experimentation or trial-and-error approaches.
Building Your Learning Plan
Create a systematic plan for applying lean startup method principles to your specific situation. This plan should include experiment schedules, measurement protocols, and decision criteria for pivoting or persevering.
Set realistic timelines for learning cycles, typically measured in weeks rather than months. The lean startup method emphasizes speed of learning over speed of execution, but rapid iteration accelerates the overall process.
Connecting with the Community
Join lean startup method communities and connect with other entrepreneurs applying these principles. Learning from others’ experiences accelerates your own application of lean principles while providing accountability and support.
Attend local startup events, join online communities, and consider finding a mentor who has successfully applied the lean startup method in their own ventures.
Embracing the Lean Startup Method for Entrepreneurial Success
The lean startup method represents more than just a business methodology – it’s a fundamental shift in how we think about entrepreneurship, innovation, and business building. By emphasizing validated learning over assumptions, customer feedback over internal opinions, and adaptability over rigid planning, this approach dramatically improves your chances of building something people actually want.
The statistics remain sobering: 90% of startups still fail, but those applying lean startup method principles consistently show higher success rates and more efficient resource utilization. The methodology doesn’t guarantee success, but it provides a systematic framework for navigating uncertainty while minimizing risk.
Whether you’re launching your first startup, developing new products within an established company, or simply trying to bring innovative ideas to life, the lean startup method offers practical tools for turning vision into reality. The key is starting small, learning fast, and remaining open to what your customers teach you along the way.
Remember that mastering the lean startup method requires practice and patience. Your first experiments may feel awkward or incomplete, but each iteration builds your skills and understanding. The entrepreneurs who succeed aren’t those with perfect initial ideas – they’re the ones who learn fastest from their customers and adapt accordingly.
Ready to begin your lean startup method journey? Start by identifying one core assumption about your business idea, then design the simplest possible experiment to test it with real customers. Document your hypothesis, measure the results, and let the data guide your next steps. Your path to entrepreneurial success begins with that first small experiment and the courage to learn from whatever it reveals.
External Source: The Lean Startup by Eric Ries – Official Website
Read Next 5 Best Chrome Extensions Productivity to Transform Your Workflow




![How to Start a WordPress Blog in 2025 [Beginner’s Guide]](https://pinewavemedia.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/Your-paragraph-text-1-1.webp)

Leave a Reply to Top 5 Viral Photo Chat GPT prompts: Professional prompts – PINEWAVE MEDIA Cancel reply